Lithium Ion Battery: Uses and applications

Batteries power everything from the portable and handheld devices like smartphones and watches to transport modes like cars and trains.
There are different types of batteries designed for different use cases.
What are lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium ion batteries are currently the most popular and widely used battery technologies.
Lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion) are a type of rechargeable battery commonly used in various electronic devices due to their high energy density, relatively low self-discharge rate, and ability to be recharged numerous times.
From tiny coin batteries used in your computer’s motherboard to large battery packs used in electric vehicles, Lithium ion batteries are used extensively.
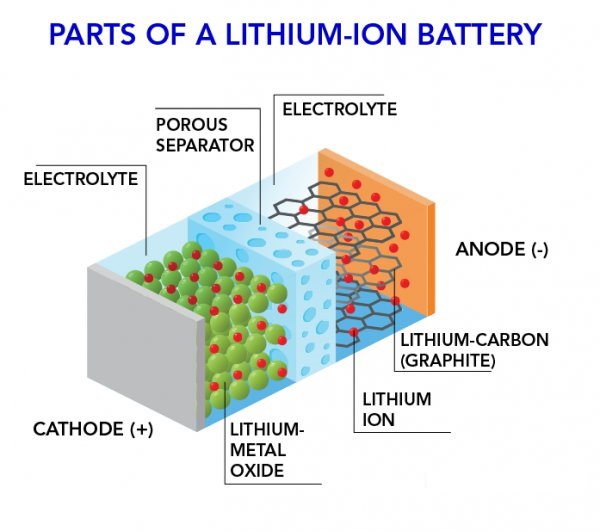
They consist of one or more cells, each containing four primary components
lithium forms the cathode and it is the chemical reactions of lithium upon contact with the electrolyte that make these batteries work.
lithium is a highly unstable element when used inside a battery’s apparatus.
Hence, a combination of lithium and oxygen together, called lithium oxide is used as the cathode.
That is because lithium oxide is a much more stable compound as opposed to pure lithium.
The cathode plays a huge role in determining the characteristics of the battery.
Both, the battery’s capacity and voltage are determined by the type of active material coated on the cathode.
The active component in this scenario comprises lithium ions. A greater quantity of these ions corresponds to increased capacity.
Moreover, a heightened disparity in potential between the cathode and anode results in higher voltage.
A porous separator is used to separate the lithium anode from the cathode. Without the separator, the battery will be highly unstable and won’t work.
The separator allows the free flow of ions from the anode to cathode while physically separating it.