Rev Up Your Knowledge: The Road To Understanding And Exploring Car Gearboxes

You might have seen your vehicle’s driver change gears when driving your car.
Have you ever been curious about the inner workings of your car’s speed and power control?
The key lies in a crucial component known as the car gearbox, responsible for enabling smooth transitions between gears and adjusting torque and speed as needed.
All vehicles have a gearbox system that requires varying torque and speed to function properly.
Even if you have a scooter which doesn’t have a manual gear mechanism, a gearbox is still present.
The most interesting part is that a gear less bicycle also has a gear (a single gear).
In this article, we’ll examine what a gearbox is, how it works, and the different types of gearboxes commonly found in cars.
What Is A Car Gearbox?
A gearbox, commonly referred to as a transmission, plays a vital role in the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels by employing various gear ratios.
Positioned between the engine and the wheels, this mechanical marvel consists of multiple gears, shafts, and bearings.
Working in conjunction with a clutch that connects it to the engine’s crankshaft, the gearbox allows for seamless gear changes by momentarily disengaging the motor and gearbox.
Its principal function is to deliver the precise amount of power and torque to the wheels at different speeds, ensuring optimal performance and fuel efficiency for the vehicle.
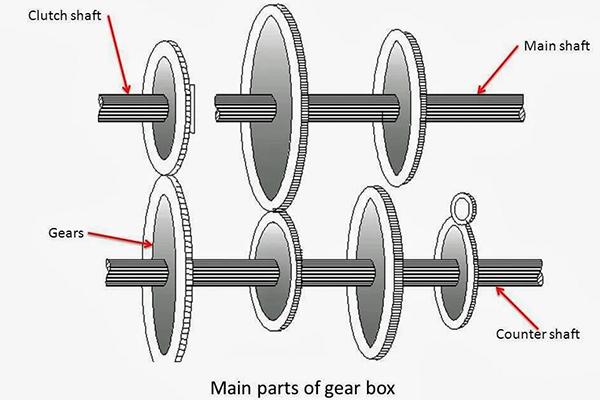
The Parts Of A Gearbox
The gearbox has evolved a lot since it was first made.
However, the parts of a modern gearbox have largely remained unchanged.
Let’s quickly examine the parts of a gearbox:
The Different Types Of Gearboxes In A Car
Car gearboxes come in two primary types: manual and automatic.
The automatic gearbox can be further categorized into several subtypes, including Torque Converter, CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission), Automatic Manual Transmission (AMT), and DCT (Dual Clutch Transmission).
Let’s take a closer look at these different car transmissions.
Manual Transmission
With a manual gearbox, drivers have full control, manually selecting gears using the gear stick and clutch.
Manual transmissions are affordable and easy to maintain compared to automatic gearbox technologies.
In a price sensitive market like India, most of the base variants of cars have manual gearboxes.
The Pros and Cons Of A Manual Gearbox
Advantages:
Disadvantages
Automatic Transmission
An automatic gearbox is a specialized type of transmission that autonomously shifts gears without the need for manual input.
It relies on electronic sensors to monitor the vehicle’s speed and operates through an Electronic Control Unit (ECU).
Compared to manual transmissions, automatic gearboxes offer greater convenience and simplicity of operation, as drivers do not need to manually engage the gears.
However, due to their increased complexity, maintenance and repairs for automatic gearboxes can be expensive.
Here is an overview of the various types of automatic gearboxes commonly found in cars.
Automated Manual Transmission (AMT)
The AMT gearbox, short for Automated Manual Transmission, is an innovative type of gearbox that automates the manual gear-shifting process by utilizing hydraulic systems to actuate the clutch pedal.
This intelligent system eliminates the need for manual clutch engagement and gear changes, as electronic sensors take charge of these functions.
The introduction of AMT gearboxes has brought about a significant transformation in the Indian car market, making affordable automatic cars a reality for many.
One of its standout advantages is its cost-effectiveness, achieved by employing fewer components compared to traditional automatic gearboxes, resulting in reduced overall vehicle costs.
The Torque Converter Gearbox represents an automatic transmission that utilizes fluid coupling to transmit power from the engine to the transmission.
Unlike other automatic transmissions, it doesn’t necessitate a clutch pedal for gear shifting.
However, in recent times, the popularity of this gearbox has diminished due to its lower fuel efficiency and relatively higher maintenance costs.
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
A CVT gearbox, which stands for Continuously Variable Transmission, operates through a pulley system.
This sophisticated transmission employs a series of intricate components to seamlessly shift between a wide range of preset gears.
The CVT system incorporates cones situated at each pulley, interconnected by a belt, and it adjusts the chain belt diameter to effectively modify gear ratios.
Known for its reliability and superior fuel efficiency, CVT gearboxes are commonly found in Japanese car models, such as Honda, Nissan, and Toyota vehicles.
Dual Clutch Transmission (DCT)
The DCT (Dual Clutch Transmission) incorporates a unique design with two clutches to optimize gear shifting performance.
By utilizing two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, it effectively minimizes gear shift lag, resulting in quicker and smoother gear transitions compared to traditional gearboxes.
While one clutch engages to deliver power, the other pre-selects the next gear, enabling rapid and seamless shifts.
Originally favored in high-performance and sports cars, DCTs are now gaining popularity in the mass-market car segment.
Prominent brands like Volkswagen, Skoda, Audi, and more have integrated DCT technology into their Indian car lineup, catering to a broader range of drivers.
The Advantages And Disadvantages Of An Automatic Gearbox
Advantages
Disadvantages